Retail Grocery Store Logistics and Inventory Management
The future of retail grocery stores will be driven by "Smart" Logistics and Inventory Management technologies using Hybrid Clouds, Big Data Analytics, and continuously vigilant Robotics and Artificial Intelligence (AI). Witness the onslaught of Amazon and Whole Foods, and Walmart, Google, and Uber changing the industry's landscape overnight with just-in-time inventories, until recently unimagined customer conveniences, and virtually eliminating store shrinkage. The technologies underlying and driving these disruptive changes are widely available to everyone today. It only remains to be seen which companies embrace them, survive and even prosper and which don't.
Retail grocery store just-in-time smart logistics and inventory management begins with each store's Inventory Management System driven by real-time data. This journey begins when the store's Inventory Management System places an order for product inventory that requires restocking. The insights offered in this paper reflect months of hands-on research with a major U.S. chain grocery store.
Our research shows that just-in-time, cloud-assisted, AI inventory management can be easily and cost-effectively implemented in any grocery store. The research further shows that the underlying technologies, Cloud AI, fisheye cameras, inventory management robotics, and customer service robotics, could be incrementally deployed with virtually no disruption to the store's legacy systems, software or workflows(1). Transparent AI components simply provide data to the store's legacy software and then uses it, in conjunction with other data in the store's system and in the cloud, for real-time analysis and decision making. The AI components might not even be installed or running on the store's system server, rather in the cloud, as a service. Finally, our research and its analysis clearly shows that reduction of shrinkage by up to 80% and increases in revenues by more than 20% are achievable, even in the early stages of incremental deployment. This paper will focus on fresh produce to illustrate how AI Inventory Management can yield such result but even more extensive application scenarios with similar, if not more impressive, results for a store's meat department, deli, bakery and other departments should be obvious.
For purposes of describing how an AI logistics and inventory management system functions, as simply as possible, this paper will profile Fresh Produce inventory for a store's Produce Floor and Fresh-Cut kiosk. Architecturally, the store has an existing Inventory Management System and Order Entry System, manually managed by the store's Receiving Department and Produce Department personnel. A Cloud interface would be installed and connected to both systems through normal Application Program Interfaces, APIs. These APIs provide the mechanisms for the Cloud AI to access and supervise both systems. Fundamentally, the Cloud AI monitors the level of store inventory for each product, in real-time and continuously, and manages the "optimal" placing and monitoring of new product orders. The objective of the Cloud AI is to ensure that the store always has the products that are in demand by its customers on its shelves while simultaneously ensuring the highest product quality, lowest product cost, optimal transportation cost, optimal in-store distribution center management and no shrinkage.
The store model we will use in this paper is illustrated here. The store is organized, from a floorplan perspective, 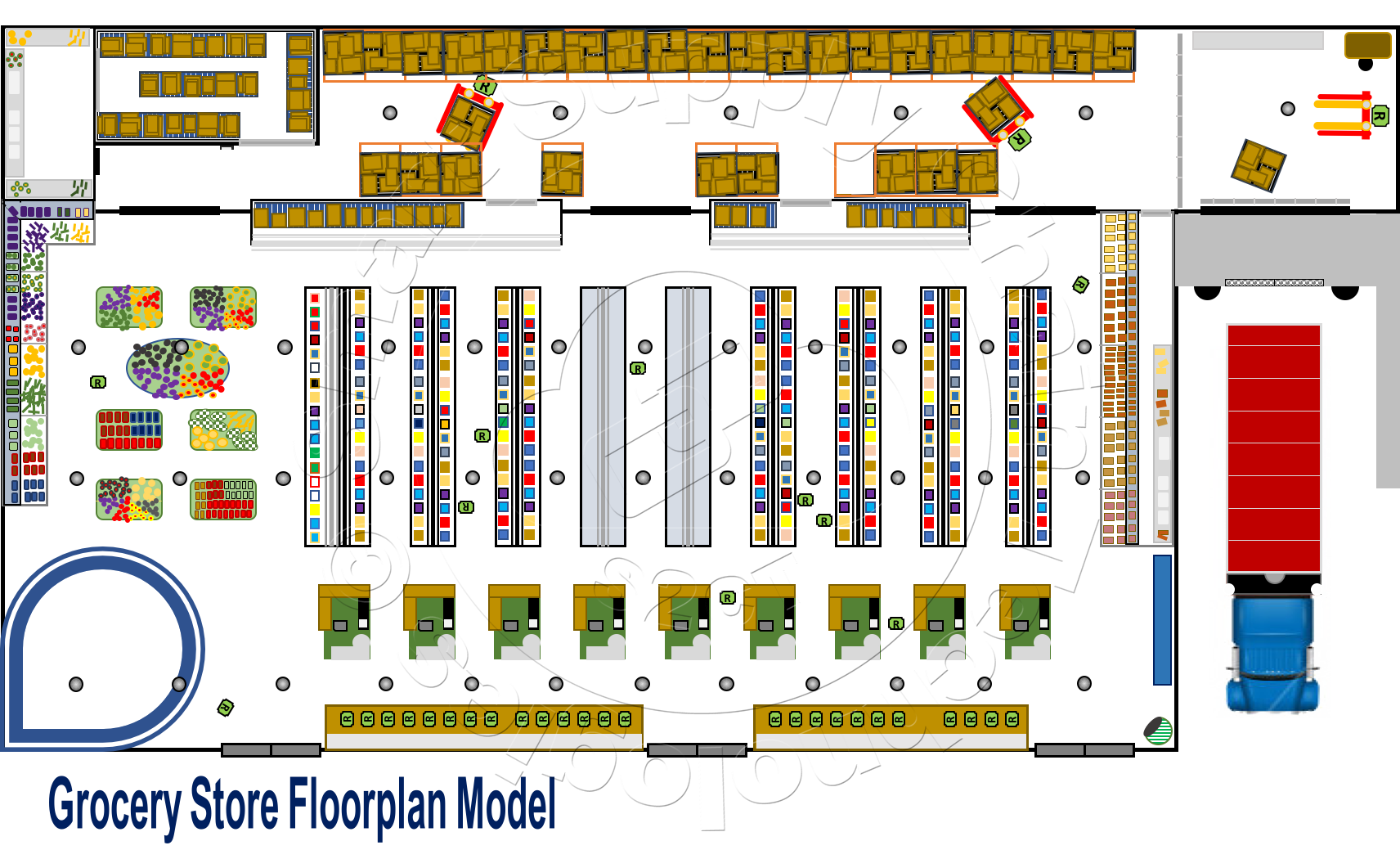 with customer checkout stations at the front of the store near the exits, the shelf aisles and Produce Tables behind the checkout stations, and the store's inventory storage area at the rear of the store behind normally closed doors. This traditional store layout has been slightly modified, in its inventory storage area, to accommodate Cloud AI Inventory Management and robotics.
with customer checkout stations at the front of the store near the exits, the shelf aisles and Produce Tables behind the checkout stations, and the store's inventory storage area at the rear of the store behind normally closed doors. This traditional store layout has been slightly modified, in its inventory storage area, to accommodate Cloud AI Inventory Management and robotics.
The key to inventory management and reaching the full potential of just-in-time inventory is accurately knowing what customers want to buy and making sure that those products are in the store and ready to be sold. This begins with the effective and efficient use of the in-store inventory storage areas. Inventory Management Robots that work behind the scenes are integral to this success. 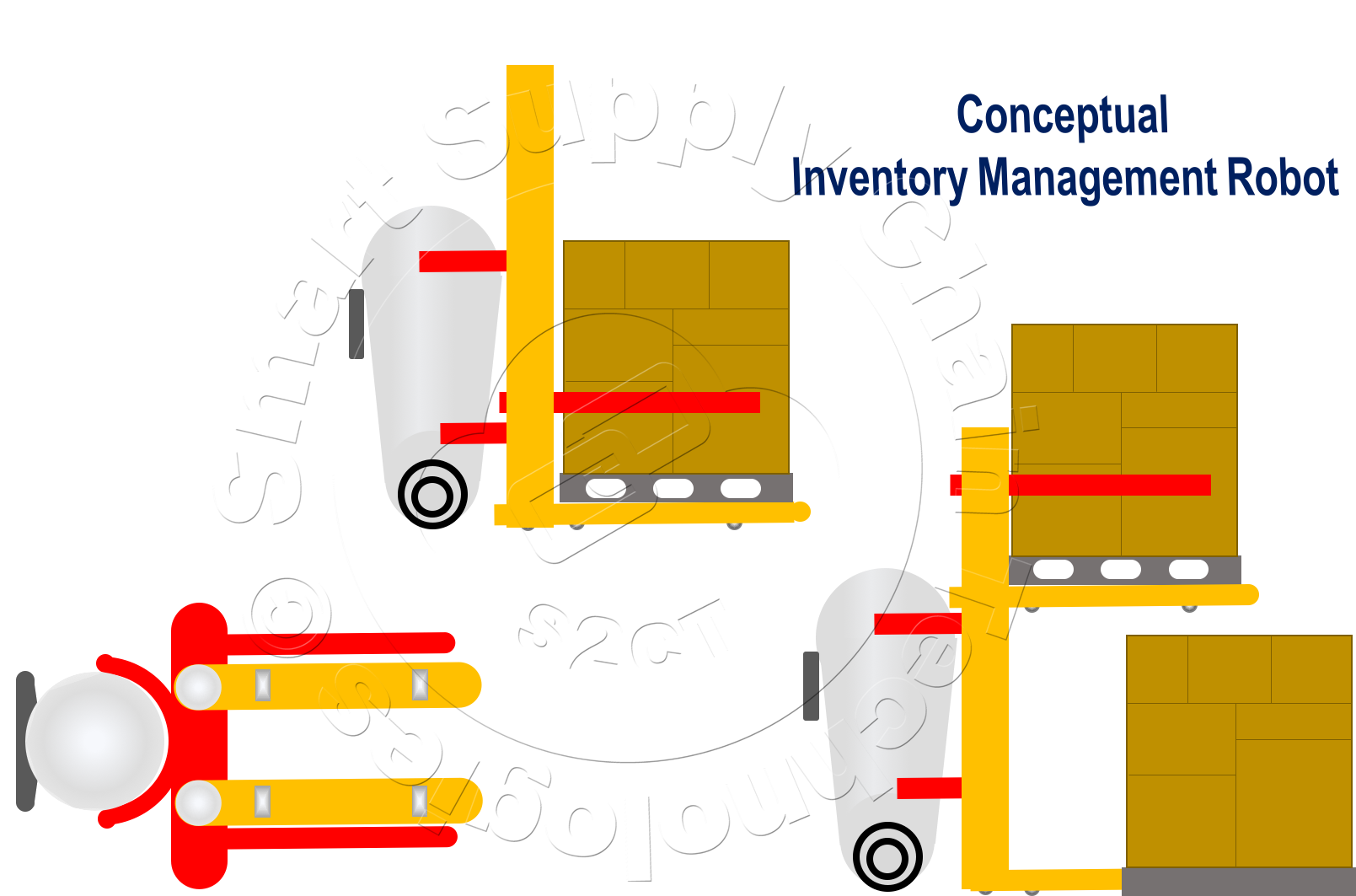 These cloud-assisted autonomous robots can receive the store's arriving products in the receiving area, evaluate what is being delivered against what has been ordered, issue a change-of-custody Blockchain ledger entries for the store and the shipper, and then manage the inventory in the store's inventory storage areas, on the shelves, to compost, or through the checkout counter. These robots can even break down pallets into their boxes, locate and scan the barcode on each box and inspect each box for critical damage. Once a delivery is accepted, an Inventory Management Robot, communicating with the Inventory Management System, moves the palletized inventory into the store's inventory storage area.
These cloud-assisted autonomous robots can receive the store's arriving products in the receiving area, evaluate what is being delivered against what has been ordered, issue a change-of-custody Blockchain ledger entries for the store and the shipper, and then manage the inventory in the store's inventory storage areas, on the shelves, to compost, or through the checkout counter. These robots can even break down pallets into their boxes, locate and scan the barcode on each box and inspect each box for critical damage. Once a delivery is accepted, an Inventory Management Robot, communicating with the Inventory Management System, moves the palletized inventory into the store's inventory storage area.
The store's inventory storage area is typically a long and wide corridor running across the width of the rear of the store. This is a temperature controlled area isolated, from the receiving area by hanging climate barriers, to protect it from the fluctuations caused by exposure to the outside ambient while receiving deliveries. The store's inventory area main cold-storage unit is typically on the far side of the inventory storage area, opposite the receiving area to further minimize the temperature impacts of proximity to the receiving area. The temperature closer to the receiving dock is allowed to reach as high as 12°C (54°F). The temperature in the inventory storage area, close to its cold-storage unit, is typically around 7°C (44.6°F), adequate for short-term produce staging. The cold-storage unit temperature should be set between 2°C (36°F) and 7°C (44.6°F), according to FDA data, https://www.fda.gov/food/resourcesforyou/consumers. Managing the ambient temperature for multiple kinds of Produce is a complex task. Monitoring these temperatures, in real-time, and reporting them to the Inventory Management System, is critical to reducing product shrinkage. Strategically placed real-time sensors and roving store robotics are perfect for this task. In our research, the store kept its Produce cold-storage unit temperature between 2°C (36.0°F) and 4°C (39.0°F).
This inventory storage area, in our example floorplan, has been partitioned into double high pallet slots along both of its sidewalls. The store's long inventory storage corridor is used to store products, typically in palletized form, until they are moved to the retail floor or into the area's cold-storage unit. The store's Inventory Management System AI assigns warehouse slots to incoming pallets based on available slots, the pallet's product ambient temperature requirements, proximity to specific cold-storage units, projected slot demand for other products not yet to arrive, etc. This is a continuous process which often requires that the Inventory Management Robot redistribute pallets in the inventory storage area throughout the day, including into the cold-storage units for diary, meat, and produce and to floor staging areas. Product pallets, being moved into cold-storage units, are broken-down to box-level, their barcodes scanned, by the Inventory Management Robot. Each cold-storage unit in the inventory storage area has an interactive display, close to its door, that store personnel can use to find what products are in them. Boxes of Produce, for example, in the main cold-storage area are further organized to be easily assessable for moving to the produce floor or into the store's Fresh Cut Room. The store's Inventory Management System AI is keeping track of inventory in the inventory storage area and cold-storage units to ensure that they are all moved out of inventory storage to retail locations before their "package-by" dates expire. This monitoring, by the Inventory Management System's AI, continues after products are moved to various retail locations around the store to ensure that they are sold or removed from the shelves before their "sell-by" dates. Again, the Inventory Management System's AI objective is to ensure that the store always has the products that its customers want and that they don't expire before being purchased. To this end, the store employs other AI technologies in its retail areas.
High Definition Fisheye Cameras have been positioned throughout the store, at strategic locations, to provide images of all the inventory on the store's shelves and kiosks. A fisheye camera captures hemispherical images of its field of view,  from the center point of its lens out 90 in both directions.
from the center point of its lens out 90 in both directions. 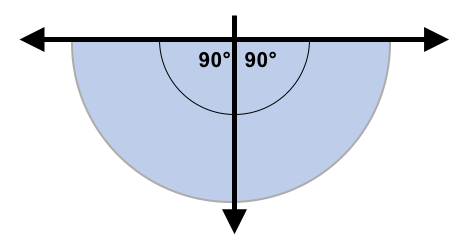 When positioned between and above two shelves, the camera will capture the image of both shelves, from the floor to essentially the height of the camera. These fisheye cameras capture images and deliver them to the Inventory Management System's AI software for processing. Processing means converting the fisheye images into normal landscape images and then, with image recognition AI software and product data, identifying the products on the shelves. AI software can recognize Fresh Cut product packages on the shelves that were made to prespecified recipes or even ad hoc packages of random Produce, blackberries, blueberries and dates in shrink wrapped tray for example. This technique will be between 90% to 100% accurate depending on a number of somewhat uncontrollable variable. It's difficult to be certain what product is in a package that has fallen over on a shelf or even more difficult when it's left by a customer, wrong side up, in an unrelated store location, from images. The Inventory Management System can request assistance from store personnel or, if equipped, from a store Customer Service Robot dispatched specifically for the investigation or opportunistically as it passes by the troubled location while assisting a customer.
When positioned between and above two shelves, the camera will capture the image of both shelves, from the floor to essentially the height of the camera. These fisheye cameras capture images and deliver them to the Inventory Management System's AI software for processing. Processing means converting the fisheye images into normal landscape images and then, with image recognition AI software and product data, identifying the products on the shelves. AI software can recognize Fresh Cut product packages on the shelves that were made to prespecified recipes or even ad hoc packages of random Produce, blackberries, blueberries and dates in shrink wrapped tray for example. This technique will be between 90% to 100% accurate depending on a number of somewhat uncontrollable variable. It's difficult to be certain what product is in a package that has fallen over on a shelf or even more difficult when it's left by a customer, wrong side up, in an unrelated store location, from images. The Inventory Management System can request assistance from store personnel or, if equipped, from a store Customer Service Robot dispatched specifically for the investigation or opportunistically as it passes by the troubled location while assisting a customer.
The primary role of a Customer Service Robot(2), designed to be able to pass through store aisles without causing any more congestion than a typical customer,  is to assist customers with in-store shopping experiences. Customer Service Robots, from their station in the front of the store, near the store's entrances, will greet customers entering the store. These connected robots have both embedded AI capabilities, like autonomous navigation, image capture, speech synthesis, data collection, and assimilation, etc., and Cloud AI capabilities, like face recognition, voice recognition, search capabilities, etc.
is to assist customers with in-store shopping experiences. Customer Service Robots, from their station in the front of the store, near the store's entrances, will greet customers entering the store. These connected robots have both embedded AI capabilities, like autonomous navigation, image capture, speech synthesis, data collection, and assimilation, etc., and Cloud AI capabilities, like face recognition, voice recognition, search capabilities, etc.
Upon greeting a customer, the Customer Service Robot will attempt to recognize the customer's face and or voice in order to personalize the greeting. If unsuccessful, the robot might attempt to use the store's cloud to successfully recognize the customer. If recognition fails, the robot might, with the customer's permission, register the customer's face and voice data in the cloud for future reference and proceed with the greeting.
From this point, there are numerous customer assistance scenarios that might unfold between the Customer Service Robot and the customer. The robot can check with the store's cloud to retrieve the customer's shopping list, sent earlier or saved in a recurring list in the customer's profile. The robot might connect to the customer's home digital assistant to retrieve the shopping list and even temporarily take on the customer's home digital assistant persona. Once connected, the robot could perform any task that the assistant might perform for the customer, answer general, check that the home's doors were locked and the lights were turned off, etc. The robot could keep track of where the customer's car was parked. Of course, the robot would be able to retrieve the shopping list from the customer verbally or from the customer's smartphone.
The Customer Service Robot can inform the store of products on the customer's shopping list that might need to be replenished on the shelf from the store's inventory area before the customer gets there. The robot can inform the customer of products on the list that are not immediately available in store and suggests available alternatives or offer to have the product delivered to the customer later in the day. The robot can point out sales and promotions and even provide digital coupons that will be redeemed at the checkout. The store's Customer Service Robots can guide customers through the entire shopping experience, even providing and navigating the grocery cart. Of course, the robot can answer any product question, how much sugar is in this product, when was this fish delivered to the store, is there an equivalent product with less sodium, where is this product from, etc. No wasted time searching for products and 100% grocery list satisfaction while preserving all of the desired in-store experiences and much more. Get to see and touch the strawberries before buying them.
As Customer Service Robots carry out their primary duties, they also transparently scan the store's retail areas for anomalies and Inventory Management System directed investigations. The Inventory Management System has continuous real-time inventory data and with its Cloud AI, knows exactly when to order more inventory to keep the store's shelves full of the products that customers want.
Returning to our Produce inventory storyline, a Produce order is triggered by the Inventory Management System's AI analytics after it determines that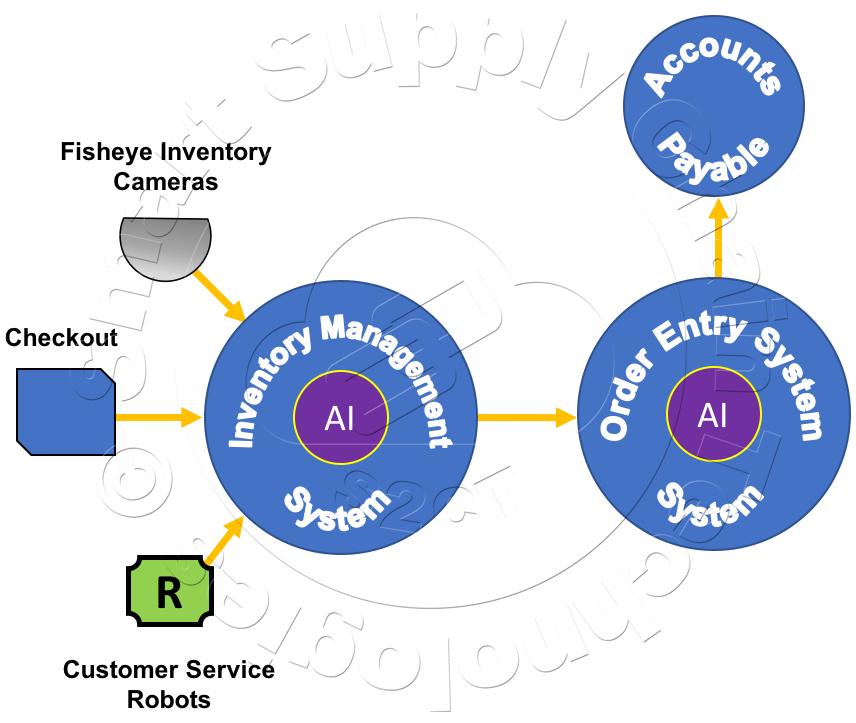 the store's inventory level of a particular product has fallen below the level necessary to meet the AI projected demand. Key to the Inventory Management System's AI projections is not only knowing the store's accurate and real-time product inventory levels, provided by the store's fisheye cameras, customer service and inventory management robotics and data from the store's checkout registers, but also having access to extensive external data related to each product's general availability from various suppliers, and the probability of their on-time delivery to the store.
the store's inventory level of a particular product has fallen below the level necessary to meet the AI projected demand. Key to the Inventory Management System's AI projections is not only knowing the store's accurate and real-time product inventory levels, provided by the store's fisheye cameras, customer service and inventory management robotics and data from the store's checkout registers, but also having access to extensive external data related to each product's general availability from various suppliers, and the probability of their on-time delivery to the store.
Produce Order Entry
Produce Arrival
 alerts store receiving dock manager of arrival and of any receiving dock congestion through Wi-Fi enabled tablet devices and their Store Operations Console App
alerts store receiving dock manager of arrival and of any receiving dock congestion through Wi-Fi enabled tablet devices and their Store Operations Console App
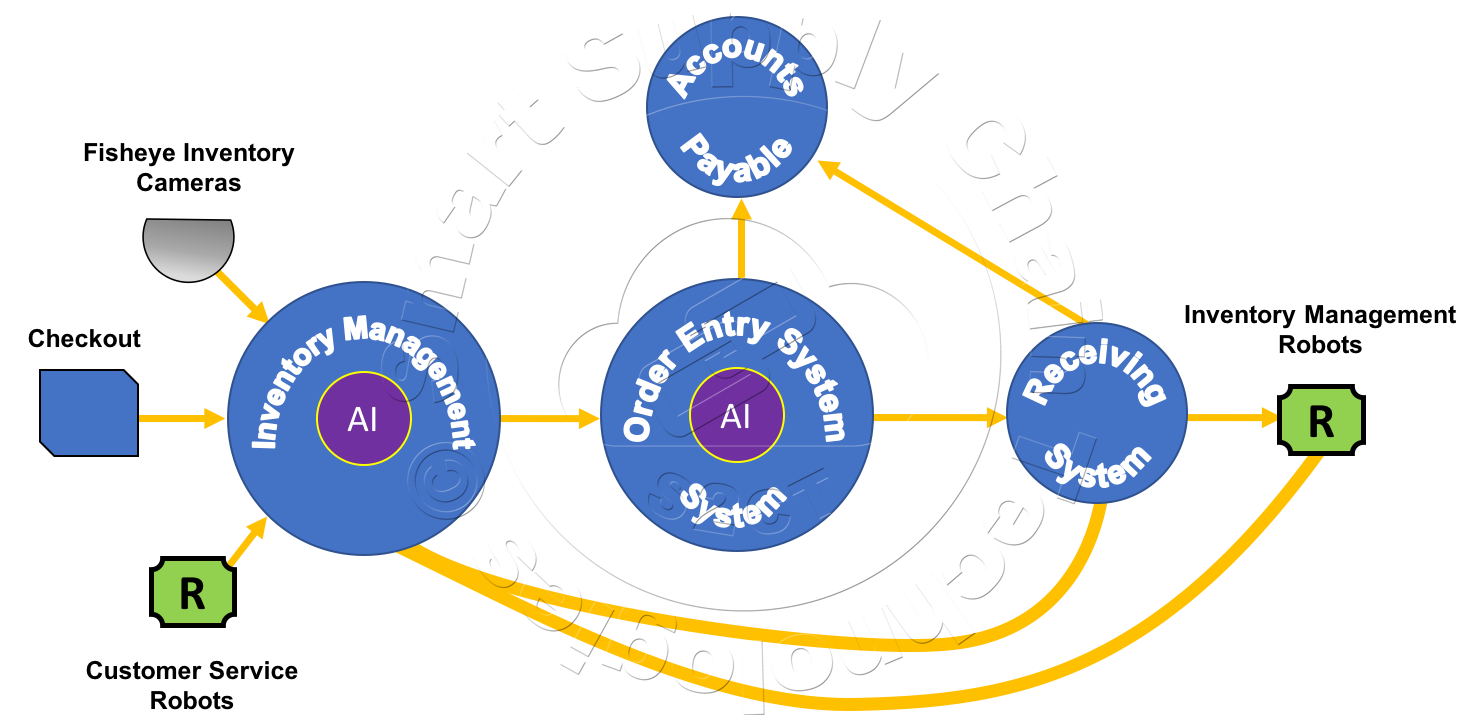
The complete Grocery Store Inventory Management System and its Dataflow are illustrated below. The Inventory Management System, using real-time data from store cameras, Inventory Management and Customer Service Robots, and the store's Checkout System keep track of the store's product inventory levels. The Inventory Management System's AI uses the store's real-time inventory data, store historical sales and shrinkage data, special consideration data, and shared product supplier data to trigger the Order Entry System to place new orders.
The Order Entry System's AI manages the order supplier selection, manages order consolidations, manages the placing of an order with a selected supplier, monitors the selected supplier's progress, reacts to delivery issues to ensure just-in-time arrival of ordered products, and manages the delivery traffic at the store's receiving dock.
The Receiving System manages the order's arrival and handling in the receiving area, manages order verification and inspection, manages the order's movement by Inventory Management Robots into the store's inventory storage area and cold-storage units, manages the removal of compost pallets from the store's inventory storage area.
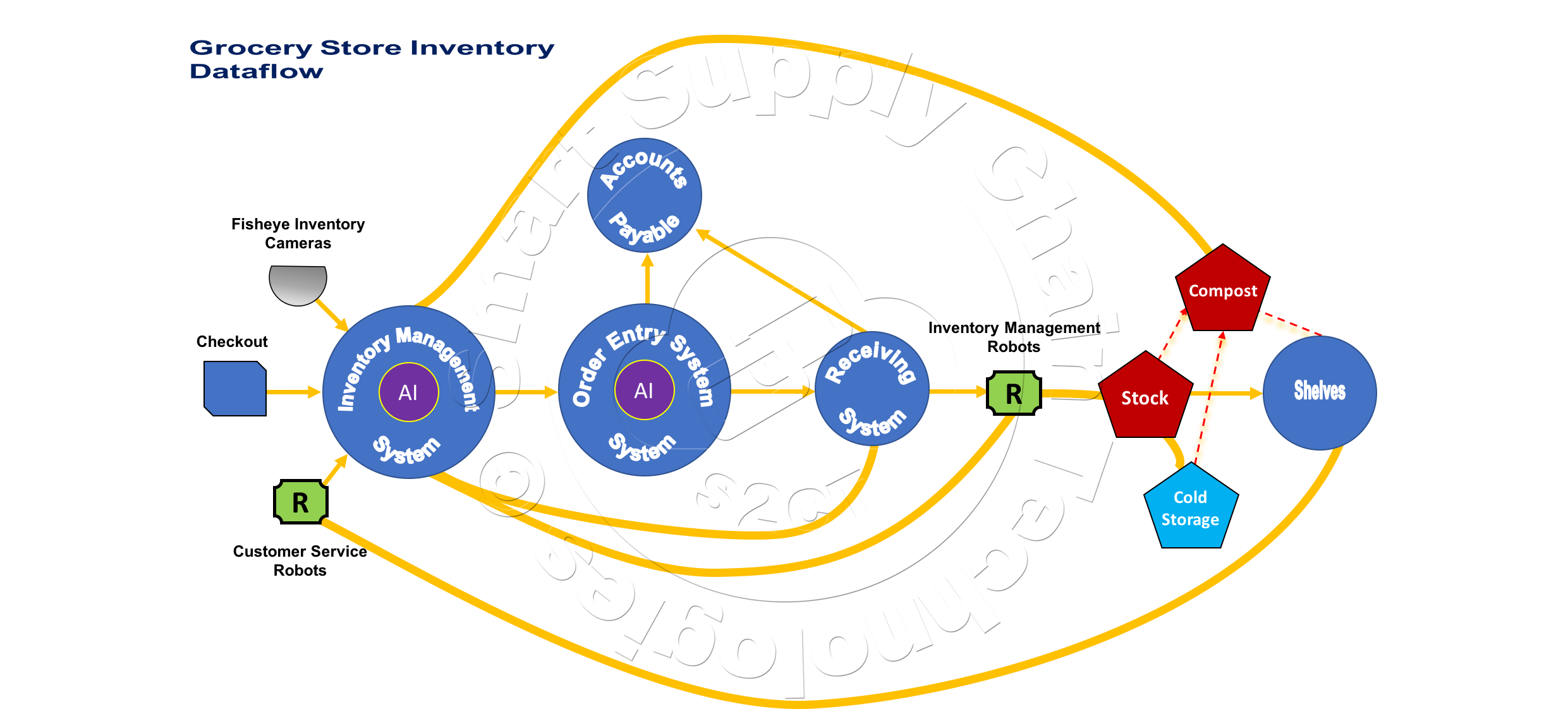
All this to ensure just-in-time store inventories, maximize store revenues by focusing on having the products in stock that customers want to purchase and minimize store inventory shrinkage by not having more than customers will purchase. Data and AI Analytics are the keys to this success!
(1) This image illustrates a typical store's legacy Inventory Management System. The collection and inputting of inventory data in the traditional legacy system is enhanced by continuous real-time data provided by the store's AI Fisheye Inventory Cameras and AI robotics. 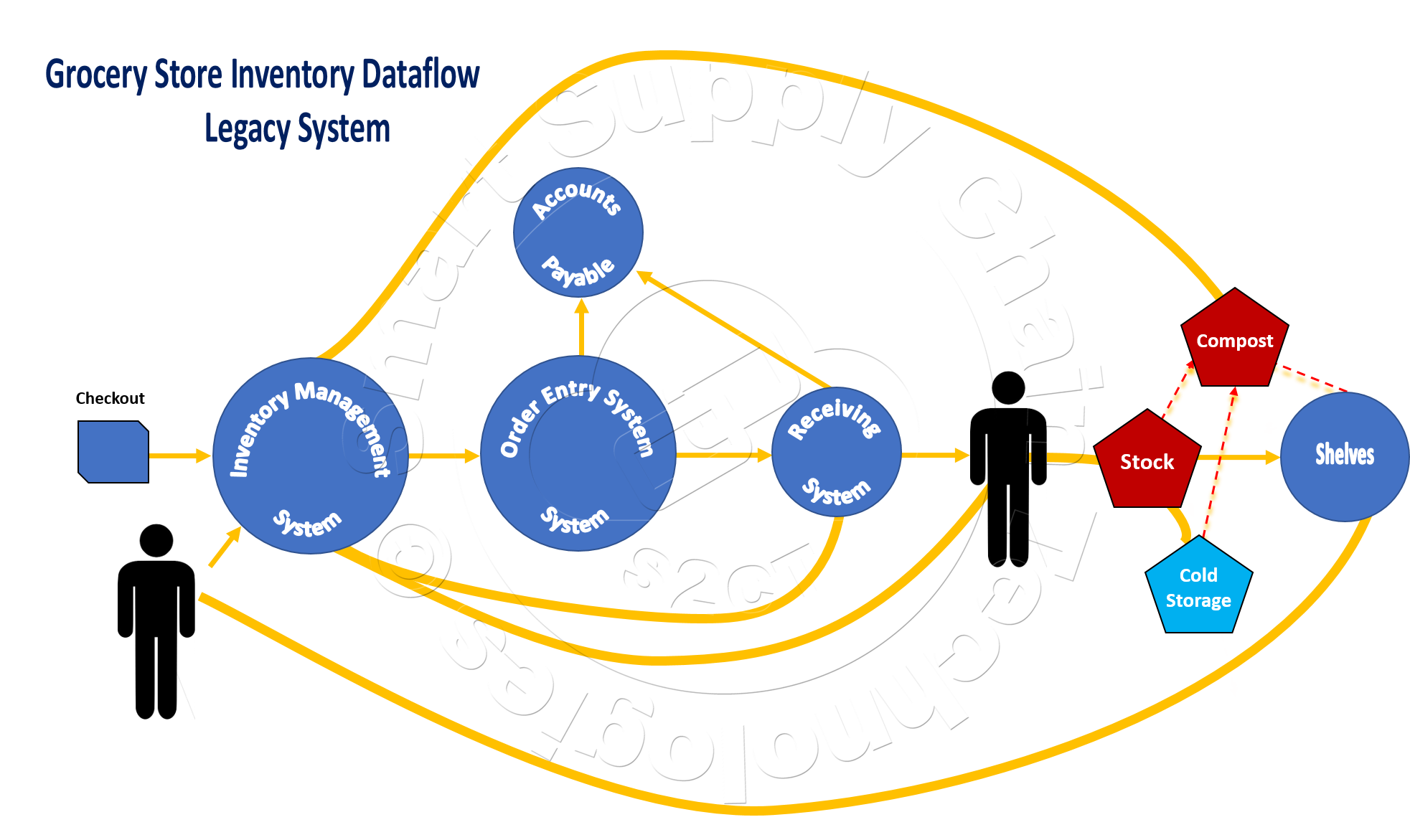 These AI devices transparently collect and sent their data to cloud AI software for processing. The AI software processes, and in some cases augments, the data and then enters it into the legacy system in much the same way that a person would. Transparent System Integration from a legacy system's perspective. The Inventory Management and Order Entry perceive and deal with the AI provided data in exactly the same way they would deal with data from another software program or data entered by a person at a terminal. Similarly, the backstage Inventory Management Robot, also transparently connected to its own AI system, for all practical purposes performs its task in the same way a person might, albeit receiving data, instructions, and sending data to the Inventory Management System, continuously, in real-time and without exception.
These AI devices transparently collect and sent their data to cloud AI software for processing. The AI software processes, and in some cases augments, the data and then enters it into the legacy system in much the same way that a person would. Transparent System Integration from a legacy system's perspective. The Inventory Management and Order Entry perceive and deal with the AI provided data in exactly the same way they would deal with data from another software program or data entered by a person at a terminal. Similarly, the backstage Inventory Management Robot, also transparently connected to its own AI system, for all practical purposes performs its task in the same way a person might, albeit receiving data, instructions, and sending data to the Inventory Management System, continuously, in real-time and without exception.
(2) An alternative Customer Service Robot Grocery Cart with the same robotic and AI features, voice synthesis, voice recognition, image recognition, side fisheye image capture and autonomous navigation,  incorporated into a traditional shopping cart. Many of those features will be integrated into the cart's push bar, cameras, display, speakers and microphone, etc. The push bar would be connected with the cart's robotic unit at the base of the cart, between its wheels. This robotic cart would perform exactly as described in the paper's narrative but would like and operate very much like a traditional cart. A familiar look and feel, stealthily performing its robotic tasks while assisting customers. These carts could even take groceries to a customer's vehicle and then return themselves to the store's cart area.
incorporated into a traditional shopping cart. Many of those features will be integrated into the cart's push bar, cameras, display, speakers and microphone, etc. The push bar would be connected with the cart's robotic unit at the base of the cart, between its wheels. This robotic cart would perform exactly as described in the paper's narrative but would like and operate very much like a traditional cart. A familiar look and feel, stealthily performing its robotic tasks while assisting customers. These carts could even take groceries to a customer's vehicle and then return themselves to the store's cart area.
(3) A variation of the Robotic Customer Service IoT Shopping Cart depicted and described in footnote 2, is a simpler, less-intrusive, clamp-on Shopping Cart IoT Bar that features all the same "key" IoT AI functionality as the robotic concept without the autonomous navigation but retaining its location-awareness.  S2CT's conceptual design clamps onto to a traditional shopping cart's bar and telescopically extends to reach the ends of the cart's original ends. The "anchor" end of the telescoping bar could house a fisheye camera that captures and sends shelf inventory images to the store's inventory management software, augmenting the store's overhead fisheye camera network. The S2CT conceptual design is battery operated and uses S2CT's IoT AI Battery Management Software to get months of battery life from a few C Cells. This battery life can even be further extended when the auxiliary power from the cart's movement, off loads the full demand on the batteries. The basic IoT Bar includes the high-value, must-have features: customer-voice-recognition, persistent-personal-assistant-persona and voice with private conversation capability, interactive shopping list management with "AI-Stock-Reserve" and communications with store's inventory management system, store aisle navigation with AI route management to guide customers to products with cart item distribution consideration (heavy and cold items last), paperless at-register coupons, sales, alternative products, interactive product information, expiration date analysis, etc. The S2CT conceptual design features dual-key data security for both customer and store data as well as physical security for the Cart IoT Bar and cart itself. The customer is never dissatisfied, always gets the shopping list fulfilled.
S2CT's conceptual design clamps onto to a traditional shopping cart's bar and telescopically extends to reach the ends of the cart's original ends. The "anchor" end of the telescoping bar could house a fisheye camera that captures and sends shelf inventory images to the store's inventory management software, augmenting the store's overhead fisheye camera network. The S2CT conceptual design is battery operated and uses S2CT's IoT AI Battery Management Software to get months of battery life from a few C Cells. This battery life can even be further extended when the auxiliary power from the cart's movement, off loads the full demand on the batteries. The basic IoT Bar includes the high-value, must-have features: customer-voice-recognition, persistent-personal-assistant-persona and voice with private conversation capability, interactive shopping list management with "AI-Stock-Reserve" and communications with store's inventory management system, store aisle navigation with AI route management to guide customers to products with cart item distribution consideration (heavy and cold items last), paperless at-register coupons, sales, alternative products, interactive product information, expiration date analysis, etc. The S2CT conceptual design features dual-key data security for both customer and store data as well as physical security for the Cart IoT Bar and cart itself. The customer is never dissatisfied, always gets the shopping list fulfilled.